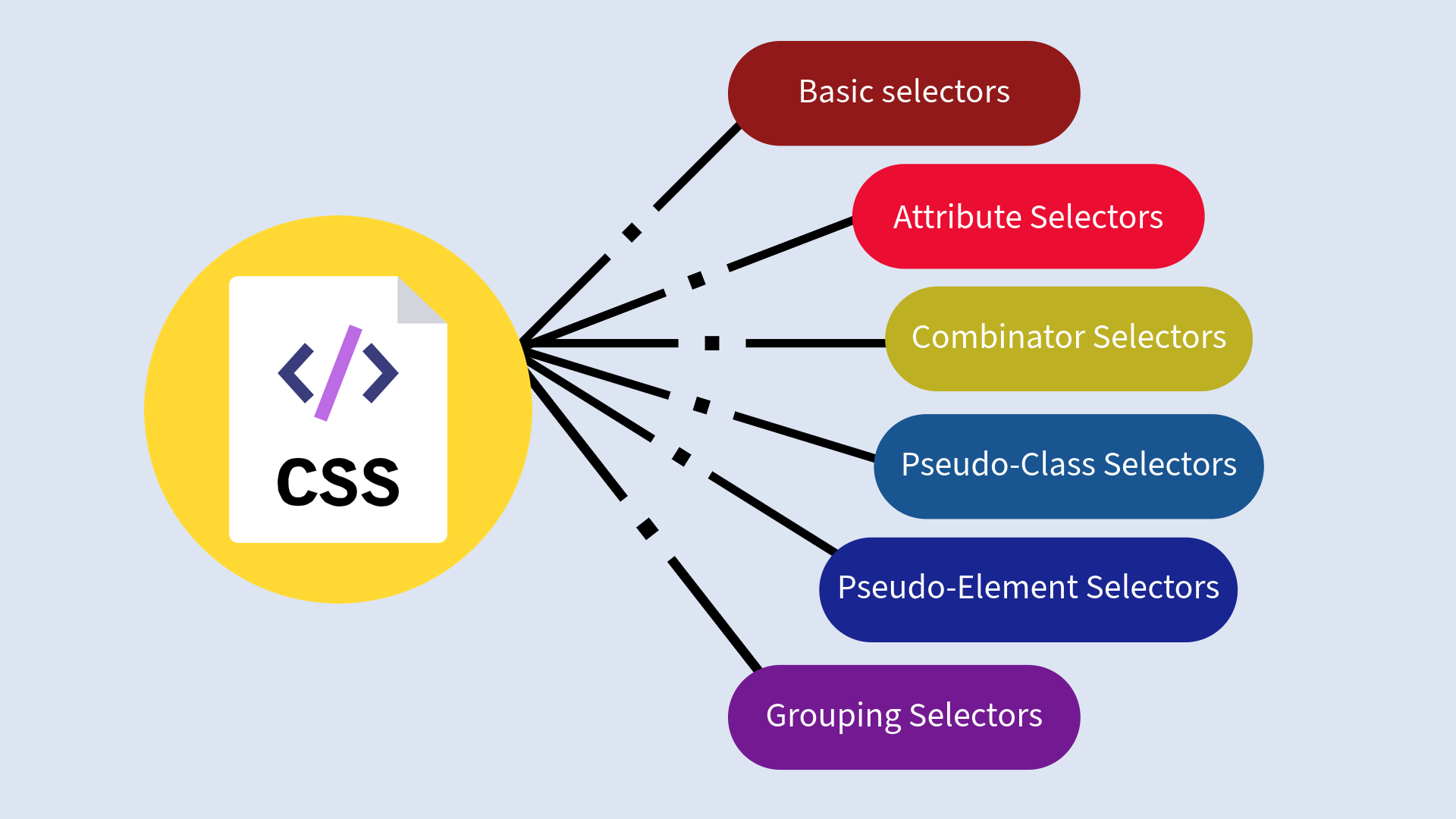
CSS selectors work basically to help you “find” HTML elements you want to style. The six selector types in CSS are basic selectors, attribute selectors, combinator selectors, pseudo-class selectors, pseudo-element selectors and grouping selectors.
- Basic selectors: These select elements based on the name, ID, or class.
- Attribute selectors: These select elements based on an attribute or attribute value.
- Combinator selectors: These select elements based on a specific relationship between them.
- Pseudo-class selectors: These are selectors used to select elements based on some state.
- Pseudo-elements: These allow you to style and select a part of an element.
- Grouping selectors: These selectors allow you to group a number of elements and apply the same style to all of them.
CSS selectors are the patterns for selecting elements and describe their style in HTML. In general, it is a fundamental part of CSS that contains a predicate to match HTML elements and apply the style rule accordingly. There are quite a few types of selectors used for different types of cases.
1. Basic Selectors
Element Selector
Selects all elements of a given type.
p {
color: blue;
}- Selects all
<p>elements and sets their text color to blue.
Class Selector
Selects all elements with a specific class attribute.
.text-blue {
color: blue;
}- Selects all elements with the class
text-blueand sets their text color to blue.
ID Selector
Selects a single element with a specific ID attribute.

- Selects the element with the ID
unique-elementand sets its text color to blue.
2. Attribute Selectors
Select elements based on the presence or value of their attributes.
[attribute]
Selects elements with a specific attribute.

- Selects all
<input>elements with atypeattribute equal totext.
[attribute=”value”]
Selects elements with a specific attribute value.

- Selects all
<a>elements with atargetattribute equal to_blank.
3. Combinator Selectors
Select elements based on the relationship between them.
Descendant Selector (space)
Selects elements that are descendants of a specified element.

- Selects all
<p>elements inside<div>elements.
Child Selector (>)
Selects elements that are direct children of a specified element.

- Selects all
<li>elements that are direct children of<ul>elements.
Adjacent Sibling Selector (+)
Selects an element that is directly after another specific element.

- Selects the first
<p>element immediately following any<h1>element.
General Sibling Selector (~)
Selects all elements that are siblings of a specified element.

- Selects all
<p>elements that are siblings of any<h1>element.
4. Pseudo-Class Selectors
Select elements based on their state or position in the document tree.
Selects elements when the mouse pointer is over them.

- Changes the text color of
<a>elements to green when hovered over.
Selects the first child of a specified element.

- Selects the first
<p>element within its parent and makes the text bold.
(n)
Selects the nth child of a specified element.

- Selects the second
<li>element within its parent and sets the text color to red.
5. Pseudo-Element Selectors
Select and style a part of an element.
::before
Inserts content before the content of an element.

- Adds the text “Note: ” before the content of each
<p>element.
::after
Inserts content after the content of an element.

- Adds the text ” End of note.” after the content of each
<p>element.
6. Grouping Selectors
Selects multiple elements and applies the same styles to all of them.
Grouping Selector (,)
Applies styles to a group of selectors.

- Selects all
<h1>,<h2>, and<h3>elements and sets their text color to navy.
With so many different selectors, you would be able to fine-tune elements in your HTML documents to make great web pages in the design. If you would like to have more examples or explanations, just let me know!